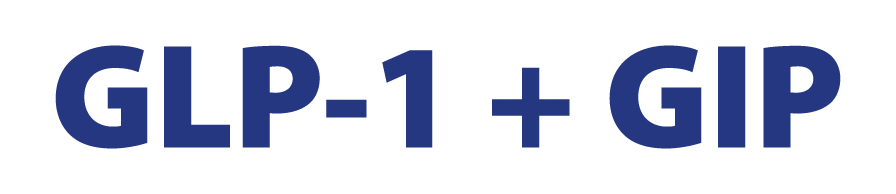Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder, which sometimes occurs outside of our awareness. Do you often wake up feeling exhausted despite getting enough sleep? Do you struggle with loud snoring or often wake up feeling breathless? These could be symptoms of a common but serious sleep disorder known as obstructive sleep apnea (OBS). In this article, we'll explore what OBS is, its symptoms, causes, methods of diagnosis, treatment options and tips for successfully managing this condition. We will also present brand new information, where it has been shown that peptide thirzepatide effectively reduces sleep apnea!

What is obstructive sleep apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated episodes of breathing stops during sleep. These breathing interruptions occur when the muscles in the throat relax and block the airway, leading to airflow disruption. These disruptions can last from a few seconds to several minutes and can occur repeatedly throughout the night. This seriously affects the quality of sleep.
Symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea
Identification symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Some common symptoms include:
- Loud snoring: Often the most noticeable symptom, loud and persistent snoring is characteristic of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Apnea episodes: Observed by a partner or family member, these pauses in breathing during sleep are a significant indicator of OBS.
- Excessive daytime sleepiness: Feeling excessively tired during the day, despite getting enough sleep, is a common symptom of OBS.
- Headaches upon awakening: Waking up with headaches or experiencing migraines in the morning can be a symptom of sleep disorders.
- Difficulty in concentration. Cognitive impairment and difficulty focusing on tasks can occur due to fragmented sleep caused by OBS.
The cause of sleep apnea is:
Several factors contribute to the development of obstructive sleep apnea, including:
- Obesity: Excessive weight, especially in the neck area, can put pressure on the airway, increasing the risk of blockage during sleep.
- Anatomical factors: Enlarged tonsils, thick neck circumference or narrow airways can predispose individuals to OBS.
- Age: The risk of obstructive sleep apnea increases with age, as muscle tension in the throat usually decreases over time.
- Family history: Genetics may play a role in the development of OBS, and a family history of the disease increases susceptibility.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption and the use of sedatives can relax the throat muscles, contributing to airway blockage during sleep.
Diagnosis and treatment options
If you suspect you have obstructive sleep apnea, it is important to consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis. A specialist may recommend a sleep study to monitor breathing patterns and other physiological parameters during sleep.
Once a diagnosis is made, various treatment options are available to effectively manage obstructive sleep apnea. These may include:
- CPAP: The CPAP device delivers a continuous stream of air through the mask, preventing the airway from collapsing during sleep.
- Oropharyngeal Apparatuses: These devices are designed to keep the airway open by repositioning the jaw or tongue during sleep, reducing the risk of blockage.
- Lifestyle modifications: Losing weight, quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed, and sleeping on your side can help alleviate OBS symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when other treatment options fail, surgical intervention may be recommended to address the anatomical problems contributing to the airway blockage.
Thirzepatide reduces sleep apnea
Nowadays, there have been completely new research, where it was confirmed that the use of the peptide thirzepatide can protect against sleep apnea.
According to the main data from two phase III trials, thiothrombopeptide injections reduced the severity of sleep apnea in obese patients, regardless of the use of positive airway pressure (PAP).
In the SURMOUNT-OSA 1 study focusing on patients not receiving PAP treatment, thiothiazepatide reduced the average number of apnea and shortness of breath events by 27.4 per hour compared to baseline measurements with an average reduction of 4.8 per hour in the placebo group. This represented a reduction from baseline of 55% compared with 5% for placebo.
SURMOUNT-OSA 2 study, which involved a population using PAP, showed that thiothiazepatide led to a mean reduction in the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) from baseline measurements of 62.8% compared with 6.4% for placebo treatment.
What else is worth using for sleep apnea?
In addition to medical treatment, there are many lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies that can help effectively manage obstructive sleep apnea:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Losing excess weight can reduce the severity of OBS symptoms by relieving pressure on the airway.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at consistent times each day can help regulate the sleep cycle and improve its quality.
- Sleep on your side: Sleeping on the back can aggravate OBS symptoms by allowing the tongue and soft tissues to collapse into the airway. Sleeping on your side can help keep the airway open.
- Avoid alcohol and sedatives: These substances can relax the throat muscles, increasing the risk of airway blockage during sleep.
- Practice good sleep hygiene: Create a relaxing evening ritual before bed, avoid stimulating activities before bed, and make sure your sleep environment is conducive to restful sleep.
Sleep apnea summary
Obstructive sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can have serious consequences if left unrecognized and untreated. These days, the peptide Tirzepatide has shown effective action against apnea, with significant results in reducing the negative consequences of apnea. If you suspect you have obstructive sleep apnea, don't hesitate to seek medical advice and explore the treatment options available to you. Remember that a good night's sleep is crucial to your health and overall well-being.